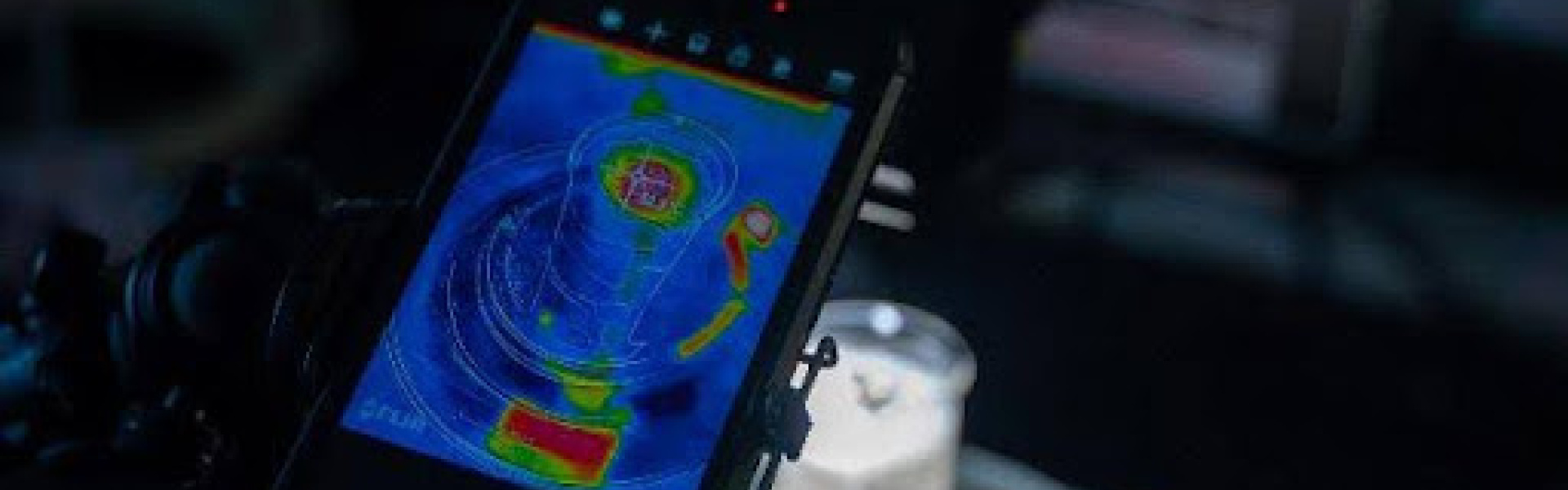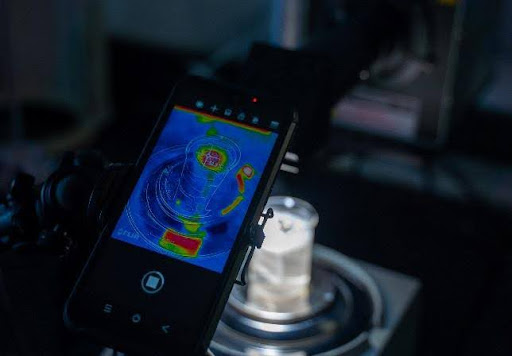
Green catalysis for clean energy research involves the development and utilization of catalysts to drive energy-related reactions with minimal environmental impact. Within this cluster, our research in solar energy explores ground-breaking advancements in electrocatalysis, photocatalysis, photoelectrochemistry, photothermal solar energy conversion, photovoltaics, and luminescent solar concentrator technologies. We are dedicated to harnessing the full potential of solar power to create sustainable energy solutions for the future. These catalysts play a pivotal role in processes such as green hydrogen production, carbon dioxide conversion, plastic valorization, nitrogen reduction, biomass conversion, and fine chemical synthesis, which are essential for transitioning towards a sustainable energy economy. Catalysts for clean energy applications often leverage renewable resources and employ innovative design strategies to enhance performance while reducing energy consumption and emissions. For example, catalysts based on earth-abundant metals, such as iron and nickel, are being developed. As such, green catalysis focuses on the use of abundant materials, the promotion of high selectivity and efficiency, and the minimization of waste generation.
Sub-elements:
- Photocatalysis
- Electrocatalysis
- Photothermal
- Photoelectrocatalysis
- Photovoltaics (PV)
- Artificial photosynthesis (water splitting and CO2 conversion)
- Green hydrogen production
- Plastic valorization
- Waste-to-energy nanotechnologies
- Plasma catalysis
- Hydrogen storage
- Fuel Cells